This means that 82% of Indians are now connected to the grid, which is almost double the numbers from the year 2000. While the Government of India and the State Governments are trying at various levels to increase access to energy, as citizens we can contribute to the effort by making the best use of the energy available to us. This website talks about one of the ways to achieve this by teaching us how to build comfortable, energy-efficient homes that meet all our comfort and aspirational wants, as well as contribute to the development and equality of our fellow citizens.
Incorporating Active and Passive Strategies in your home can yield energy savings. These savings lead to reduction in energy bills. Due to low operating costs, these savings can accrue overtime to provide home owners additional benefit. With improved efficiency, your home can see appreciation of real estate value as well. In addition to direct monetary benefits, the energy saving strategies can provide you a comfortable environment. This can lead to a positive impact on your physical and mental well-being thereby improving your productivity and reducing health related costs.
EcoNiwas calculates annual energy and cost savings for your building. It compares the energy use of your home to a typical home and applies the cost of energy (in Rs/unit) to show financial savings. Use EcoNiwas to find out which strategy can yield highest savings!
The electricity we receive at our homes uses coal. This coal is burnt at thermal power stations to generate electricity. The process releases harmful emissions into the air. Therefore, when we use electrical appliances or other electrical equipment we are indirectly releasing emissions and affecting our environment.
The energy we save goes a long way in protecting the environment. Firstly, we avoid the unnecessary emissions linked to electricity generation. Secondly, we are preserving natural resources like forests and wildlife that are affected due to mining activities. Finally, the released emissions and receding forests have health impacts on communities residing close to these mining areas.
EcoNiwas calculates the potential of avoiding emissions through energy efficiency strategies. It uses emission factor to calculate avoided emissions. Emission factor is a metric used to calculate amount of carbon-di-oxide equivalent (CO2e) emissions for every unit of electricity generated. Use EcoNiwas to find out which strategy is most helpful in avoiding emissions.
The "building envelope" of your house includes the outside walls, windows, doors, roof, skylights, etc. of your home. It is the skin of your house and helps protect everything inside it. The kind of building envelope you choose will determine how comfortable your home remains at different times of the day, night and during the year. This is because a well-designed building envelope keeps your home as warm, cool, or lit as you want for longer, so that you don’t have to use heaters, air-conditioners or indoor lighting as often.
Understanding how heat flows helps us understand how our houses’ building envelope will function. Heat moves from a warm to a cool space. This flow of heat occurs if your building envelope is not designed to suit the climate in which you live, and can cause discomfort especially during peak summer or winter, when the difference in temperature inside and outside your home is significant.

Figure1 Building envelope and energy exchange.
Heat flow, in and out of the building through its walls and roofs is faster when
Various cost effective passive design methods described below can be inculcated in the design of your homes to bring down the electricity consumption and to increase the comfort-level.
Orientation is the direction your home faces. It is usually preferred that homes are oriented towards gardens, green spaces and beautiful views. Sometimes the need for comfort also dictates how rooms are arranged, where windows are placed and when spaces are used.
Orienting the building, its spaces and windows can help you achieve naturally lit, ventilated and comfortable rooms through the day and around the year.
Orientation for Daylight
Frequently used spaces that must be well lit, such as living rooms, should face North-South.
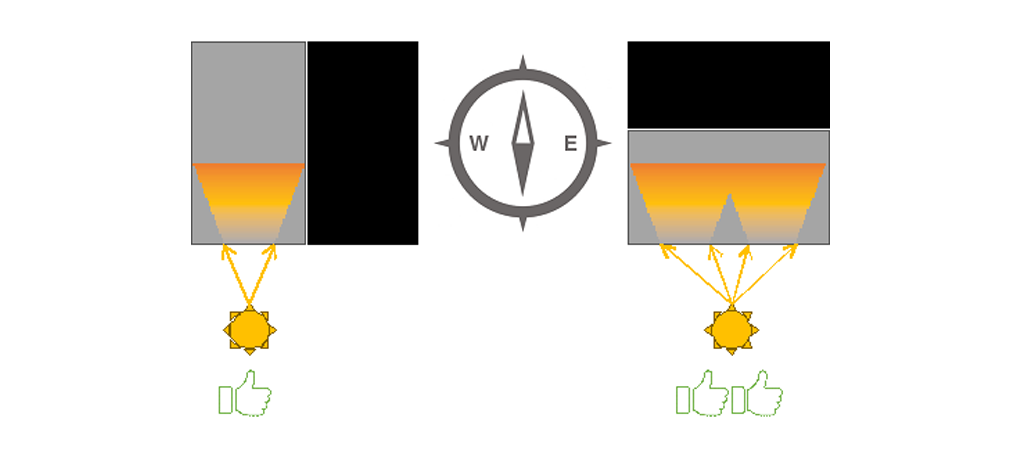
Figure2 Impact of layout arrangements and orientation
Window that face the North provide comfortable, glare free light. South facing windows also provide ample sunlight, but they will also heat up your rooms, and are especially helpful in colder climates. East and West facing windows bring in both heat and glare and should be avoided.
While windows help in bringing daylight, shading is required to get maximum benefit.
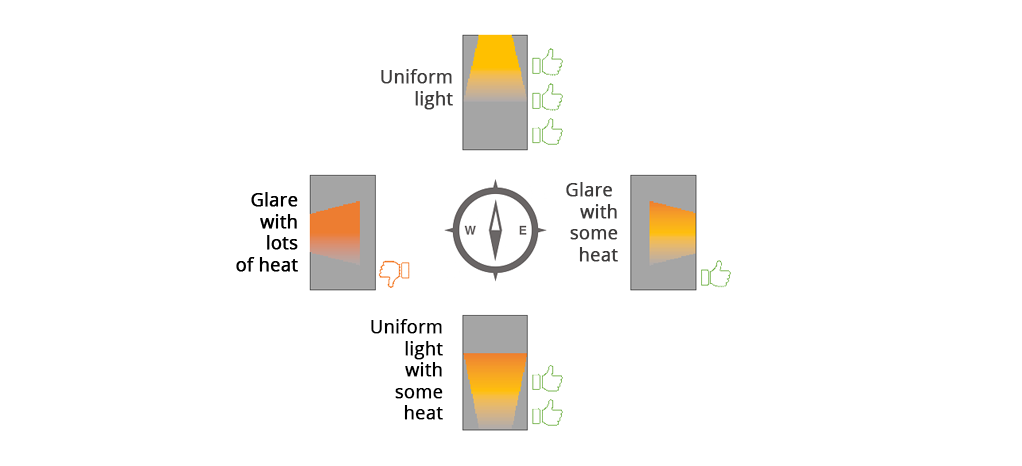
Figure3 Impact of orientation on heat and light coming into the building
Orientation for Thermal Comfort
The weather can often be harsh, either too hot or too cold. Your home can mitigate the effects of weather and orientation of your home has an important role to play. This is because the direction your house faces has affects how much heat and light it takes in.
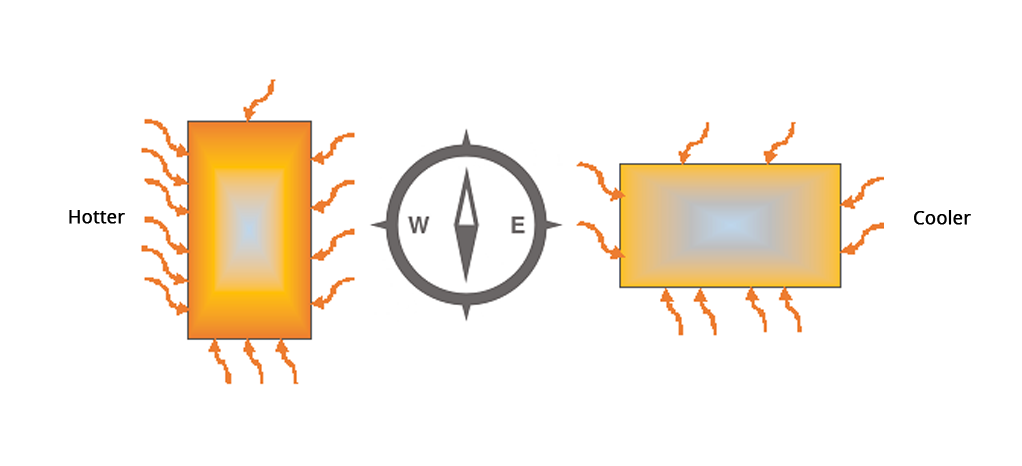
Figure4 Impact of orientation on heat flowing into a building
The rooms your family uses frequently should preferably face away from the rising and the setting sun (East and the West directions respectively). This would reduce the heat of the sun falling over the building. Only rooms not meant for longer periods of occupancy, such as store rooms, staircases, bathrooms, etcetera may face the setting sun.
Shades protect our home from direct sunlight and rain. Shades are temporary or permanent structures such as horizontal or vertical projections around the window, which protect your home from direct sunlight and rain. Even a verandah or projected roof acts as a shade.
External Shading Devices
The most effective solution for shading your home is to add an external shading device such as an overhang or a fin that would stop the sun rays from falling onto the glass surface altogether. An overhang is a horizontal projection above the window, while a fin is a vertical projection on the window sides. Both are shades that protect your windows from direct sunlight. These features must be carefully designed considering what time of the year and between what hours of the day shading is necessary for your home.
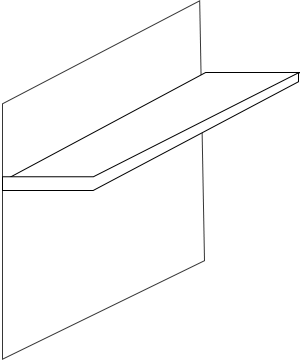
Horizontal Overhang
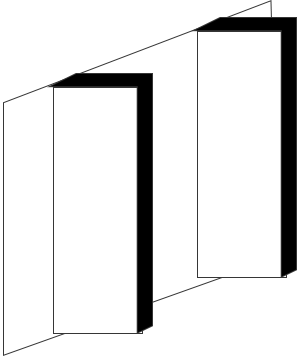
Vertical Fin
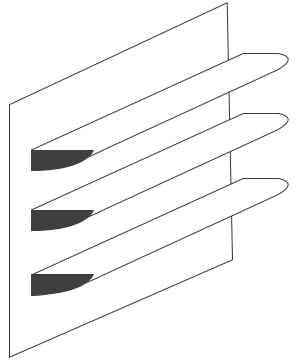
Horizontal Fin
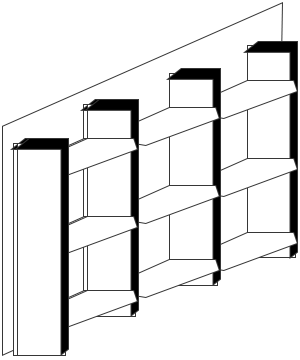
Egg Crate: Combination of Horizontal and Vertical Fin
Extended roof, horizontal overhangs over the windows are effective in shading the overhead afternoon sun (beaming in from south and south-west). Combination of fins and overhangs, and plants can used for protection from rising and the setting sun (beaming in from east and west). These devices can be designed to be fixed or moveable, so you can adjust them according to your home’s shading requirements. North facing windows require minimal shading as they do not receive direct sun for most part of the year. In cold places windows can be unshaded to receive the sun.
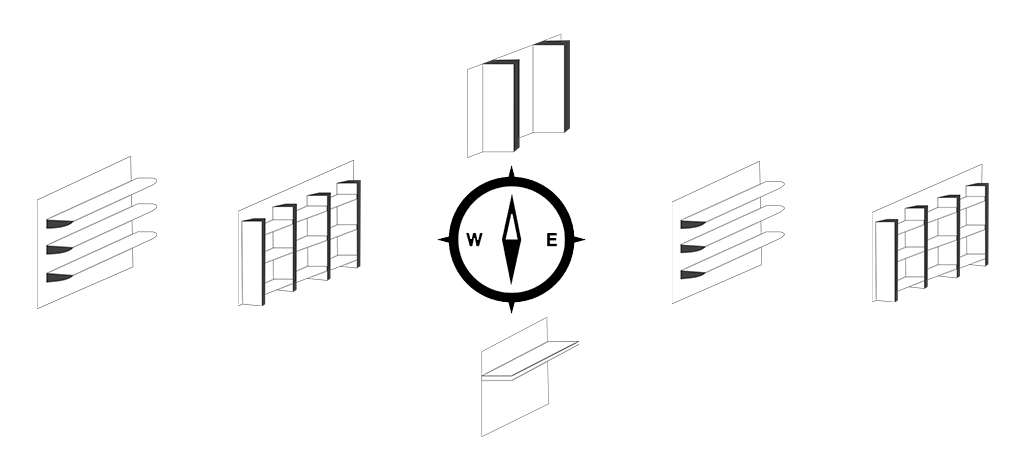
Figure6 External Shading Devices and their applicability as per orientations
Internal Blinds and Curtains
Curtains and blinds help make your home more welcoming and beautiful and can help you control the space to meet your requirements. For example, you could pull the blinds when you need an afternoon nap, but draw them away when you would like to study. However fundamentally, the external shade is your first line of defense against direct sun and heat, while the internal blinds can help you in exercising finer control over how much heat and light you want to allow into the room.
Insulation is a bad conductor of heat, i.e. it is difficult for heat to travel through it. It is applied in buildings to regulate temperature inside the home, irrespective of outside conditions. For example, in hot climates, insulation helps in limiting heat from entering the building, while in cold climates, insulation helps in keeping the heat inside the building.
When the building is not insulated, you usually use room heaters/coolers to keep your homes at comfortable temperature with respect to the outside conditions. This essentially means that there is an exchange of heat energy between your home and the outside environment. The building envelope of your home acts as a medium for this exchange. Obstructing this exchange, especially during harsh weather (summers or winters), can help you reduce your reliance over these mechanical heaters/coolers, while also reducing your electricity bills. Insulating the building envelope can help in obstructing heat exchange.
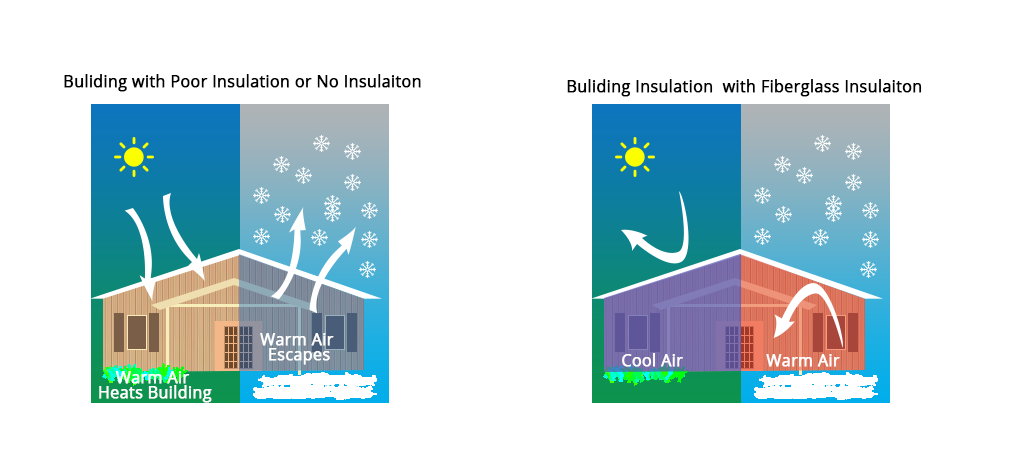
Figure8 Impact of insulation. (Insulated vs Uninsulated home)
Insulating materials can be applied on walls, roofs, windows and sometimes even the floor of your home. For walls and roofs, insulation can be achieved by:
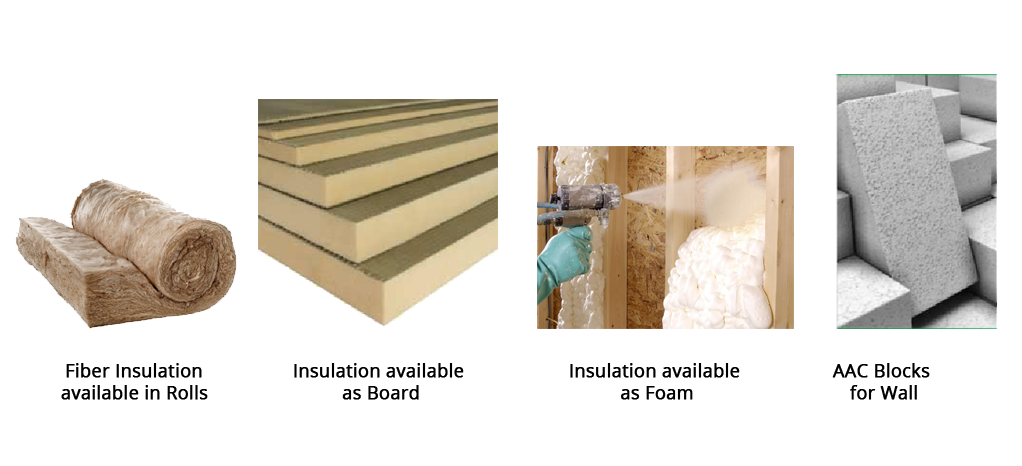

Figure9 Insulation products available for roof and wall assemblies
For windows, insulation can be achieved by selecting the right material for frames and insulated glass.
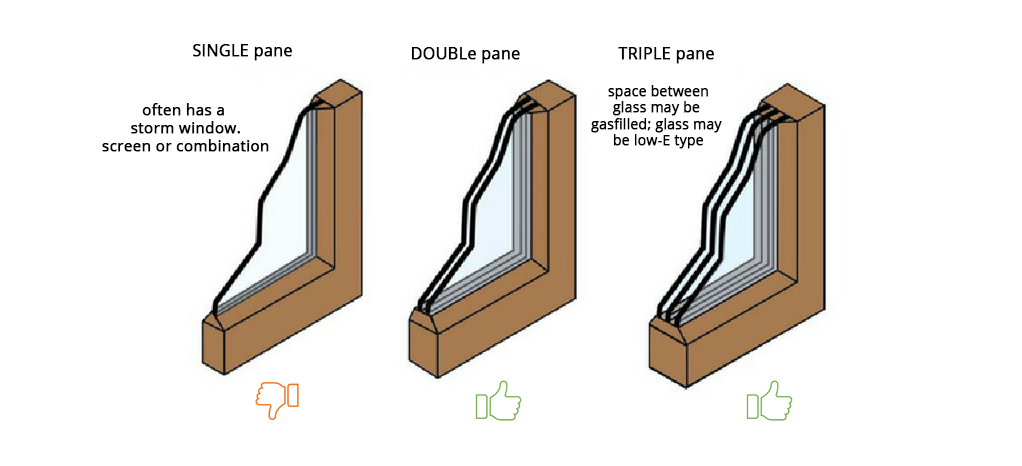
Figure10 Different glazing types. Insulated glazing is preferred (double or triple)
Glass traps some of the Sun’s heat that enters through it leading to high temperature indoor. This is the reason spaces enclosed by glass in a hot climate need increased air conditioning. Heat gain through windows can also be reduced by using special glass. With technological advancements, new varieties of glass that reduce the incoming heat have been developed such as – heat reflecting glass, tinted glass, glass filled glazing etc. However, you may wish to consider proper shading for your home first as that will effectively reduce the need for more expensive options such as these glasses. Such glasses will come to your aid in case shading is not an option for your home.
Finally, while constructing your house, you must ensure that there are no air-gaps between the wall, roof and windows. This is because air-gaps will allow air to enter your home from outside, or allow it to leave from inside your home.
Daylight is essentially sunlight. Daylight has the potential of naturally lighting our spaces during the daytime to avoid use of artificial light sources like bulbs, tube-lights, etcetera. This can help in reducing energy use, and therefore electricity bills for lighting during daytime. In addition to financial savings in electricity bills, daylight also promotes physical and mental well-being and its impact on productivity has been well established.
Daylight enters the space through windows. Mindfully placed windows, shades and room arrangements can improve the quality of daylight entering your home. You can adopt the following strategies to improve the quality of daylight in your home:
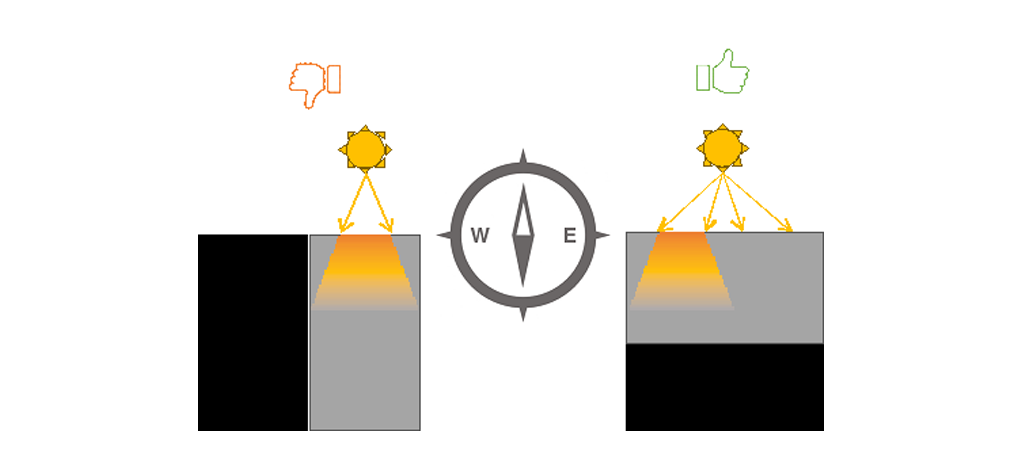
Figure11 Frequently used rooms should face outside, preferably North/South

Figure12 North-South facing rooms have better daylight quality
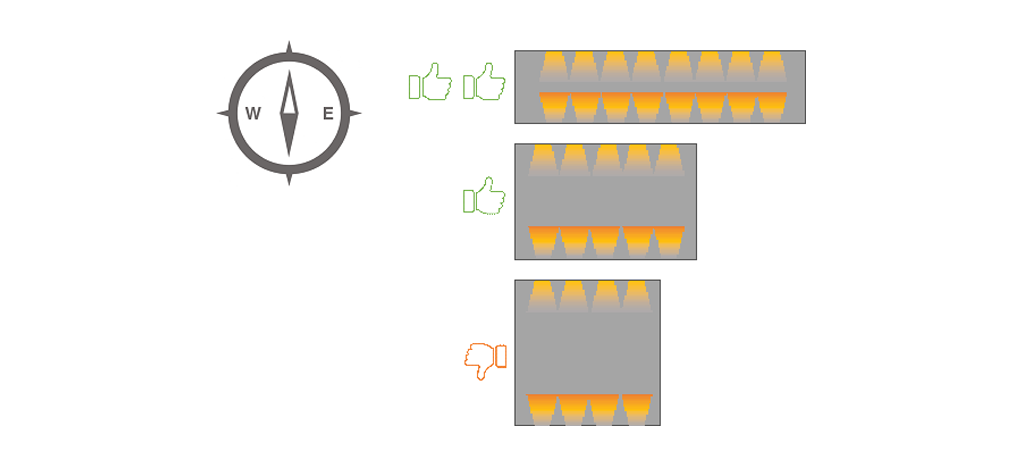
Figure13 Area being naturally lit reduces as we build deep spaces
Use of high windows (clerestory), north facing windows (north lights), reflective shades and proper arrangement of windows and integrating courtyards can improve the quality of daylight.
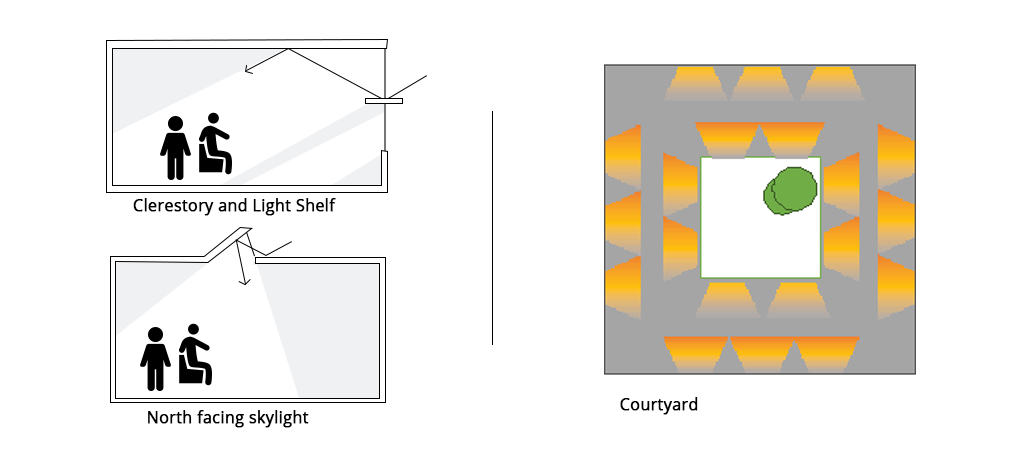
Figure14 High windows, courtyards, etcetera are few strategies that assist in improving natural light
The window area needs to be designed so as to strike a balance between natural light and the possible incoming heat through glass. Shading devices discussed earlier, along with obstructing heat from directly falling on the windows also reduce the occurrence of harsh light inside the rooms, and thus are an important aspect of climate responsive design.
We breath oxygen and exhale carbon-di-oxide (CO2), this is called the respiration process. When we are indoors, the level of CO2 in the air increases due to the respiration cycle. Along with CO2, body odor, moisture and other pollutants within the house make the air inside stale. Breathing stale air is unhealthy. To maintain freshness in space, the stale air must be replaced by fresh air regularly. Fresh outdoor air, is taken from the external environment, and the replaced indoor air in turn carries away with it the pollutants from inside your home. This process of replacing stale air inside your home with fresh air from the environment outside through windows and door openings, without the use of fans is Natural Ventilation.
In hotter places natural ventilation also help bring the room temperature down. This cooling effect can help reduce use of fans, coolers and avoid air-conditioners to significantly bring down your energy bills. You can employ the following strategies to improve the natural ventilation in your home:

Figure15 Winds flowing at suitable height improve comfort

Figure16 Strategies to improve ventilation through appropriate window placement
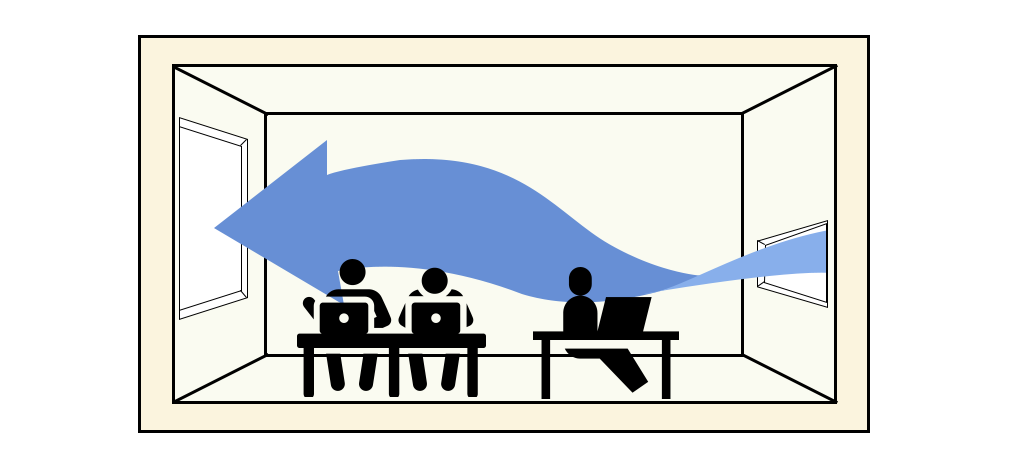
Figure17 Winds speed up as they pass from smaller to larger windows.

Figure18 Windows near the ceiling aid in removing accumulated hot air.
In humid climates such as in Coastal regions, ventilation can bring in much needed relief, because cool breeze replaces moist warm air faster away from our bodies causing the sensation of comfort. In desert like climates, natural ventilation can bring in unwanted heat as well which can cause discomfort. Wind passing over water bodies or through ‘khus’ pads, like in desert coolers, can provide cooler air. In colder areas, cold winds can cause discomfort. Obstructions around the house may be used to slow the cold winds. In the plains, which see both hot summers and cool winters, the in-between period is especially suited for natural ventilation when ‘Natural cooling’ can help avoid use of air-conditioners.
'Cool' roofs are used in hotter climates. As the name suggests they prevent heat from entering your home. The roof is exposed to sun throughout the day, it heats up during the day and passes this heat inside. As the name suggests, cool roofs keep the heat out. In case you live in a warmer climate, in addition to shading and providing insulation, selecting the right roof finish can significantly reduce the need for cooling your home. Cool roofs reflect most of the solar radiation falling on the rooftops. These can be implemented in three ways.
Green Roofs
Green roofs are gardens cultivated on terraces. The soil and the plants will help in insulating your roof, which will reduce your home's overall heating and cooling costs. These roofs can reduce “urban heat island” effect – An urban heat island (UHI) is an urban area that is much warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities. A green roof reduces the level of heat absorbed by a building, and helps reduce the UHI effect for your home. In increasingly urbanized spaces, Green roofs also provide you with easily accessible green spaces.
Reflective Surface
Your roof can be transformed into a cool roof by painting it with white reflective paint and overlaying the surface with white ceramic broken tiles etc.
Thus, installing a cool roof will reduce the need for air conditioning and make buildings more comfortable for your family.
We often use heating and/ or cooling equipment in our homes to provide a comfortable living environment for our families. In a carefully designed building, the walls, roofs, windows and interior surfaces alone can maintain comfortable interior temperatures for a large part of the year. Sometimes, however we also require a certain level of moisture (humidity), air speeds and air quality to feel comfortable and these can be achieved by mechanical systems.
Air conditioning systems transport heat, that is, they move it from one place to another. Heat is removed from a space such as your bedroom to provide cooling and released outside. Mechanical cooling permits to move heat from a place with lower temperature (inside the building) to a place with higher temperature (outside the building), which would otherwise be impossible.
Air conditioning systems consume large amounts of energy for operation leading to high electricity bills and contain refrigerants which are greenhouse gases responsible for climate change. We should aim to reduce if not eliminate our dependency on these mechanical systems. While purchasing these systems you can choose the most appropriate options for your requirements and help enhance the comfort of your home.
Most commonly used air conditioning systems for homes are :
Unitary Air-Conditioners
Unitary Air-Conditioners or Window Air-Conditioners are normally used for cooling individual rooms and provide cooling only when needed. Room air-conditioners house all the components of an air conditioning system in one box. As the name suggests they are installed in the windows.
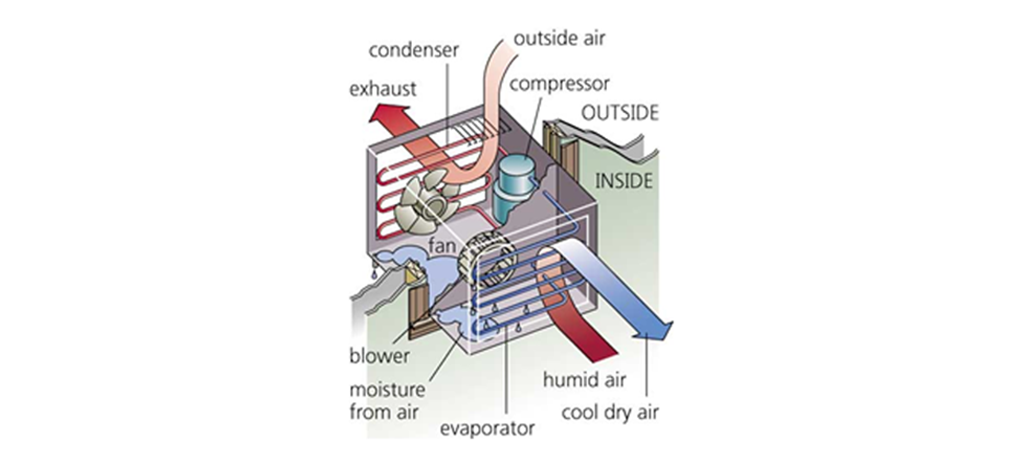
Figure19 Room air-conditioner
Split-System Air-Conditioners
A split AC system has two parts, one placed outside the room which contains the cooling equipment and another part which is placed inside the room, which contains a fan to take in heat from the room, and supply cool air.
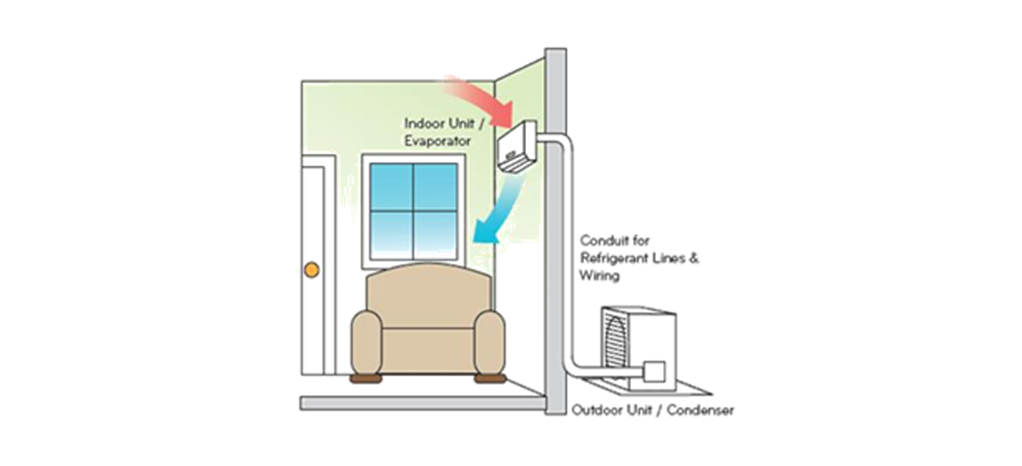
Figure20 Split air-conditioner
Packaged Air-Conditioners
A packaged air-conditioner is a bigger version of the window air-conditioner. An outdoor unit which usually is placed on a roof or on a concrete slab adjacent to the building performs the cooling functions. Conditioned Air is supplied from and warm air returned to the outdoor unit by connecting ducts through building’s exterior wall or roof.
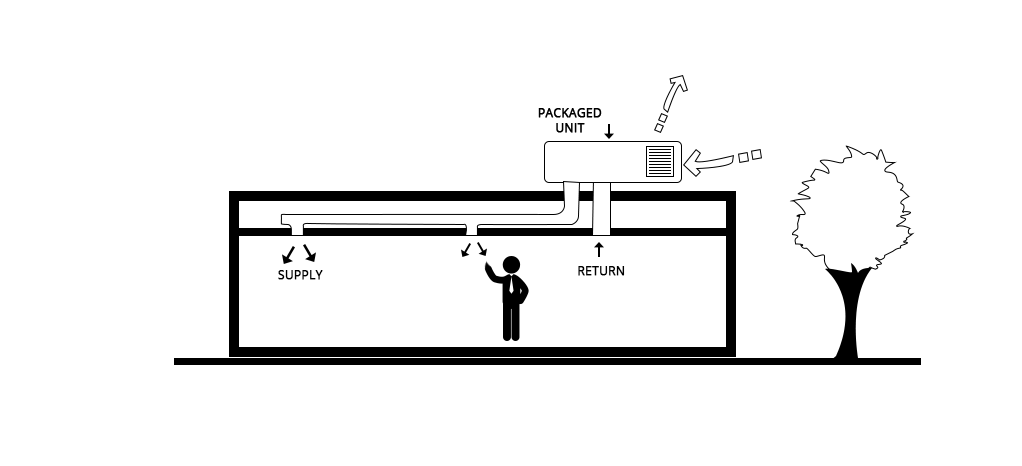
Figure21 Packaged Air-Conditioner
HVAC systems are expensive, and it is therefore important that the most optimal one be selected for your home so that it provides your family with the most comfortable living conditions. It is also important that such equipment be installed properly.
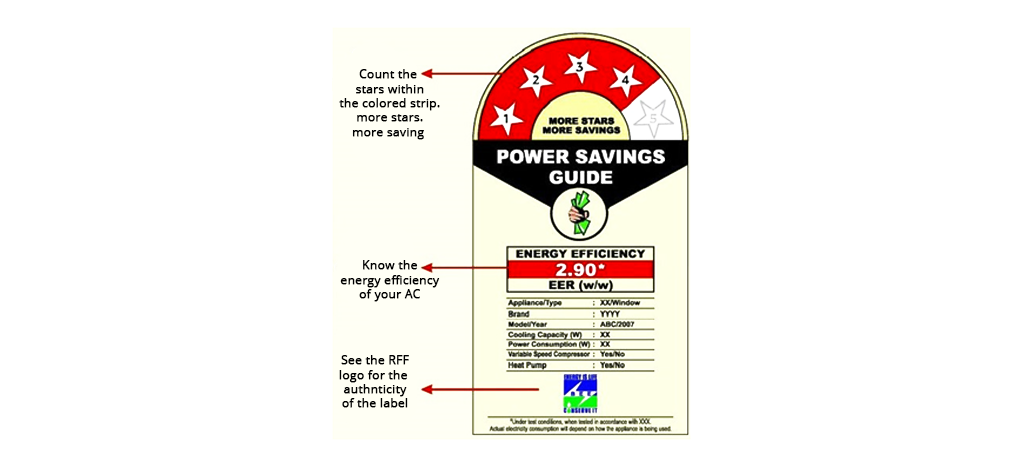
Figure22 BEE's Star Label for Room Air-Conditioner
You can still reduce your electricity bill by using Air-conditioners that have more BEE stars. The label on the air-conditioner has stars on a scale of 1 to 5. Any machine which has a star rating of 1 on this scale is the least efficient machine. A five-star AC is the most efficient AC possible, and if you purchase this air-conditioner and install is as per instructions, it should consume the least amount of electricity in comparison to any other air-conditioner. Thus, the more the stars, the less electricity such equipment should consume because it is more energy efficient.
While selecting a place to install your air-conditioners, you must make sure it is away from direct sunlight and heat, and in a shaded space. You must also always keep the filters of your air-conditioners clean to ensure that it continues to run efficiently and maintains good quality of indoor air.
Air-conditioners take the same amount of time until they reach a given temperature no matter how low their cooling temperature is set to. For example, if on a hot day you wish to make the temperature of the room more comfortable, and want your AC to help cool the room to 24°C, setting the AC temperature to 18°C will not help make the AC run faster. This is because the machine will cool your room to 18°C only after it first cools it to 24°C, and therefore will make your AC work harder for a longer period of time and consume more electricity than when set at the temperature you feel comfortable at.
Another way to ensure that your AC is running at the optimum level is to make sure you are not setting the temperature uncomfortably low, for example we set our ACs at an uncomfortably low temperature of 16-19oC for the AC and cover ourselves to keep us warm. Instead we must dress up according to the persisting weather conditions. We should make it a practice to wear light, less layered clothes at home during the summers and set the AC to a higher temperature, so that the energy consumed by the AC is reduced . People feel most naturally comfortable between the temperatures of 24- 26°C. Setting a lower temperature on your AC would also feel uncomfortable because when you step out of the conditioned room, the temperature outside would feel even warmer than it otherwise would. A third danger is that if you spend a lot of time in such low temperatures, your body will get used to living in such conditions. This means that a space which you may earlier have felt was warm, will now feel very hot to you. All these issues will lead to an over use of your air-conditioners, making them less efficient and leading to them developing mechanical faults earlier.
If we continue to set our ACs at a lower temperature, overtime our body gets accustomed to such low temperatures. A space which in the past would have been judged by us as warm will now be perceived as very hot. Our preferences would shift to having lower room temperatures leading to higher usage of AC.
Your homes can be ventilated, to circulate cool air throughout the room and avoid still hot air by using an electric fan. By using fans, the air is forced to move across our bodies faster, taking away air filled with sweat and this makes us feel cooler.
Since ceiling fans are widely used in most houses, they consume major share of energy among our electric home appliances. Energy consumed by fans is much more than that consumed by artificial lighting. Also, artificial light is used for shorter duration of time, generally when it gets dark to the time we sleep, whereas fans are used mostly throughout the day and night for ventilation. To reduce the electricity consumed by fans, BEE rated fans, which have more stars should be used. BEE star rated fans with more number of stars, may cost you a little more than a regular fan on purchase, but they will give you the benefit of reduced electricity bills over its lifetime, making it a good buy for your house.
With advancements in technology like BLDC (Brushless DC Motor) technology efficiency of fans have improved. These are capable of saving 50% of the electricity, by consuming only 30-35 watts of electricity, against conventional fans which consume 70-80 Watts of electricity.
Conventional incandescent bulbs produce light when electricity passes through its filament to heat it enough to produce light. In this process, the bulbs convert electricity to large amounts of heat and not as much useful light. Only about 5% of the electrical energy supplied is converted to light and the rest is released as heat and warms up your home.

Figure23 Efficiency comparative for lighting technologies
Of the various types of lights available in market, CFL and LEDs lamps are much more energy efficient than the regular yellow light bulbs or halogen lamps because they produce less heat while producing the same amount of useful light. The major benefits of installing CFL or LED lights in your home are that they have last longer, and they do not heat up the rooms, reducing the need for repeated replacement of your light fixtures and for air-conditioning bringing down your costs.
Significant energy savings can be achieved by a combination of automatic operations and manual switching which allow you to turn down or switch off lights when they are not needed. Oftentimes, large amounts of energy are wasted when only manual switching is resorted to for turn off lights as they are not prudently controlled. Various automatic lighting control systems that use timers and sensors can be used to turn on and off lights when needed. They are convenient, and reduce payback time period for the investment you have made in installing them through the cost of electricity saved and longer life of lamps due to reduced use by dimming or turning off lights.
T5 fluorescent tubular lamps are a new technology that offer good brightness, lifespan and are a cheap alternative to LED lamps along. They are slim and elegant in appearance as well.
Powering your home through renewable energy such as Sunlight can significantly reduce the costs of owning and living in it. Many renewable energy technologies such as photovoltaic panels, biomass, wind turbines are available for use in the residential context which can help reduce your home’s dependence on electricity supplied by the electricity grid and various power distribution companies at high prices. This will also make your home independent of the impacts of power cuts and shortages, and provide you with as much power as you require whenever you need it at a much lower cost than what you will experience with the conventional electricity grid connection.
Solar energy is free and abundant in most places in India. It also offers immense scope of applicability, adaptability (versatility over other renewable sources of energy) and ease of operations and maintenance over other sources of renewable energy. If you decide to take advantage of this resource for providing electricity for your home fully or in part, you must take the following information into account:
Solar or Photovoltaic rooftop system consists of a solar panel installed on the roof of the house. They generate power during daytime by converting sunlight directly to electricity. They can be of two types -
A 1 kW gird connected rooftop solar system can be set up over a shade free area of 10 sq m.
Photovoltaic system provide the following benefits -

Figure24 How Photo voltaics generate energy!
With advancements in technology, Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) made from thin film solar cells are available in the market. They are photovoltaic materials that are used to replace conventional building materials in parts of your home such as skylight, window shades etcetera. They generate electricity while performing other functions as a building element. The initial cost of BIPV is offset by reducing your money spent on the conventional building materials and labour required to normally construct that part of your home, as well as the much reduced electricity costs over the lifetime of your home.
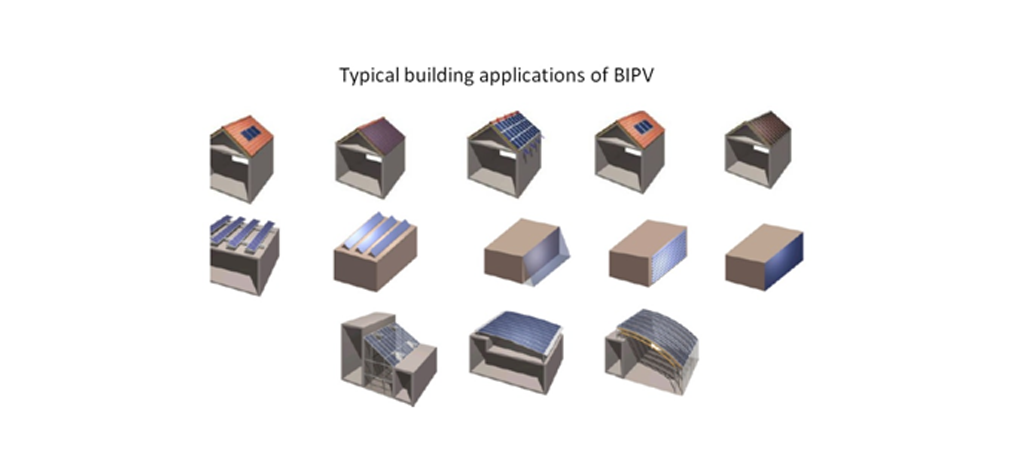
Figure25 Building Integrated Photo-voltaic applications
The energy from sunlight can be used to heat water in homes. A solar hot water heater does the same. It consists of several solar collectors installed in open spaces, roofs which get sunlight. Water which is heated is stored in a tank capable of retaining the heat, to be used for various daily activities like washing, bathing etc.
For homes, the solar heater system without a pump shall suffice. The system can run efficiently unless cloudy conditions do not persist for over a day or two. Und er such weather conditions, an electric system integrated with the solar hot water system shall be serve as a backup.
A solar water heater for a family of 3- 4 shall be of 100 litres per day capacity, taking up 1.5-2 sq.m of space on the terrace/open space. It can save up to 1,500 units of electricity a year for you.
Depending on various factors like weather conditions, location of your city, system efficiency etc the soft water running through the system can attain a temperature of upto 60-80 °C . Solar hot water heater can supply hot water even when electricity is not available and does not produce pollution as in case of heating water with firewood or other fuels.
It is useful to keep track of your home’s energy use. Energy use can be tracked by periodically monitoring the information on your energy meters. Monitoring your energy use can influence conscious decisions on purchase and use of appliances and other energy consuming equipment. Nowadays, smart meters are available for home-owners. These devices can connect to your smartphones and give almost real-time updates on energy use.
Other than knowing your overall energy use, you can also benefit from knowing your energy use by components. Like each household is metered separately, each circuit within the house maybe metered separately as well. This is known as sub-metering.
It is a fluorescent lamp, commonly used as an energy efficient alternative to traditional bulbs. It is available in various shapes (spiral, tube, etcetera).
Daylight is natural light from the sun that lights up the room. In context of this website daylight is referenced as alternative to electric lighting during daytime.
Emission Factor is equivalent emissions generated in burning a unit of the fuel.
Fenestration is an opening in the wall or roof for ventilation, daylight or views. Windows and skylights are fenestrations.
Fin is a vertical shading device. This is used to shade the window from direct sun.
Material that resists transporting heat. In context of this website, insulation is a bad conductor of heat. Insulation is applied to roof and wall to avoid heat loss/gain.
kW is a unit of power. It is also a measure of electricity demand.
kWh is a unit of Energy Use. In billing terminology, 1 kWh is referred as a ‘Unit’ of energy use.
Label is a mark provided to equipment that meet energy efficiency benchmarks. In India, Bureau of Energy Efficiency is responsible for providing labels for various equipment.
It is one of the latest lighting technologies that uses semi-conductors to generate light. It is one of the most energy efficient lighting technologies available today.
Overhang is a horizontal projection above the window. This is used to shade the window from direct sun and rain.
If your home is built to suit the climate it is in, it will be well suited to your family’s needs. This means it will not require as much heating, cooling or lighting and will be more comfortable and healthier to live in. Such buildings are called “Passively Designed”. Passive buildings respond to the local climate and use less electricity as compared to conventionally designed buildings. In addition to being comfortable and cheaper to operate, these buildings also fetch better returns in the real estate market.
Photo Voltaic is panel of semi-conductors that converts light into electricity. Photo voltaic uses sunlight to generate electricity. This is a clean and renewable source of energy.
Smart meter is a device that is capable of recording electrical parameters (energy, demand, etc.) and providing this data in a digital format.
Split air conditioner is a cooling device mounted on the wall. As the name suggests, the air conditioner is split into two parts; fan coil unit and outdoor unit. The fan coil unit collects the heat from the room and transfers it to the outdoor unit by a fluid called refrigerant. The heat received by the outdoor unit is released outdoors.
T5 is a fluorescent lamp in the shape of a tube. It is called T5 since its diameter is 5/12th of an inch. Modern T5s operate on an electronic ballast (choke).
Window air conditioner is a cooling device mounted on the window that operates on electricity. It takes the heat from the room and dumps it outside in order to cool the room.
Click here to check compliance
© 2025 ECO-NIWAS. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.